vApp Networks
Overview¤
In addition to virtual data centre (VDC) networking, you can create individual vApp networks to have even greater control over your network infrastructure.
vApp networks enable you to create smaller networks within individual vApps that have a vApp edge, like the edge gateway on your VDC. Although a vApp edge is not as feature rich as a VDC edge, it enables you to create firewall and NAT rules to separate your VDC networks from your vApp virtual machines (VMs). This means you can create some quite complex networks to satisfy application needs.
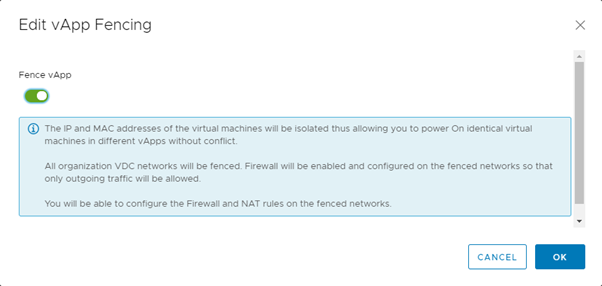
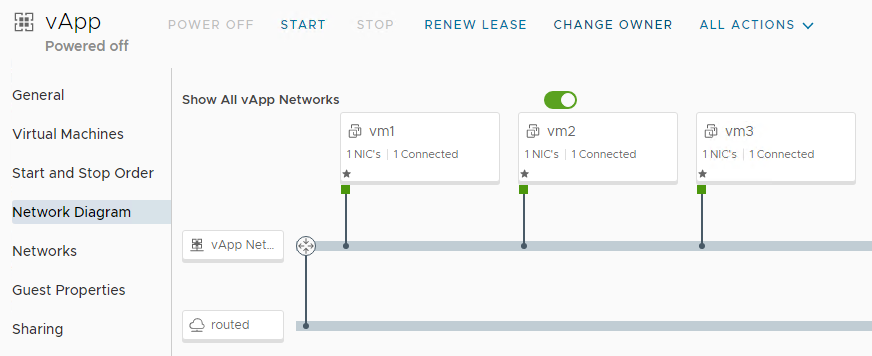
The vApp network diagram below shows the vApp edge:
Creating a vApp network¤
-
In the VMware Cloud Director Virtual Datacenters dashboard, select the VDC that contains your vApp.
-
In the left navigation panel, select vApps.
-
In the card for your vApp, select Actions, then Add network.
-
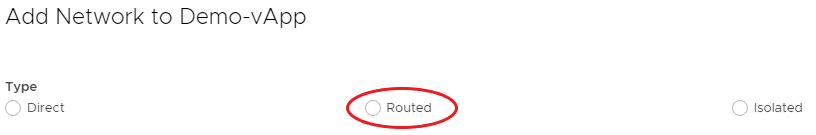
In the Add Network dialog box, select vApp Network.
-
Enter a Name and Description for the network.
-
In the Address and DNS section, fill out the fields as required for your network.
-
When you're done, click Add.
Connecting a VM to a vApp network¤
If your vApp is already populated with VMs that are connected to a VDC network, you may want to move them over to the vApp network.
To change the network a VM connects to:
-
In the card for the vApp, select Details.
-
In the Virtual Machines section, Click each VM, under Hardware and in the NICs section, click edit and select the vApp network from the Network list.
-
If you want to dual-home your VM, click the NEW button to add a second network.
-
When you're done, click Save.
-
You can go back to the VM hardware properties to see the new IP address assigned to the VM.
Viewing and adjusting vApp network settings¤
When you've created your vApp network and assigned VMs to it, you may want to review the vApp network settings and adjust them if needed.
-
In the left navigation panel, select vApps.
-
In the card for the vApp, select Details.
-
Select the Networks tab.
-
Click your vApp network to view its network settings.
-
The General tab displays general network settings. Click Edit to adjust these settings.
-
The IP Management tab lists the IP settings for the network, including static pool and DNS and DHCP. Click Edit to adjust these settings.
-
The Services tab enables you to set up firewall and NAT rules for your network. For more information, see How to create firewall rules.
-
The Routing tab enables you to create static routes for your network. For more information, see How to create a static route.
Enabling DHCP¤
DHCP is not enabled by default.
To enable DHCP:
-
In the left navigation panel, select vApps.
-
In the card for the vApp, select Details.
-
Select the Networks tab.
-
Click your vApp network to view its network settings.
-
Select the IP Management tab then DHCP.
-
Click Edit.
-
In the Edit network dialog box, select the Enabled option.
-
Enter IP Pool and lease information for your DHCP addresses then click Save.
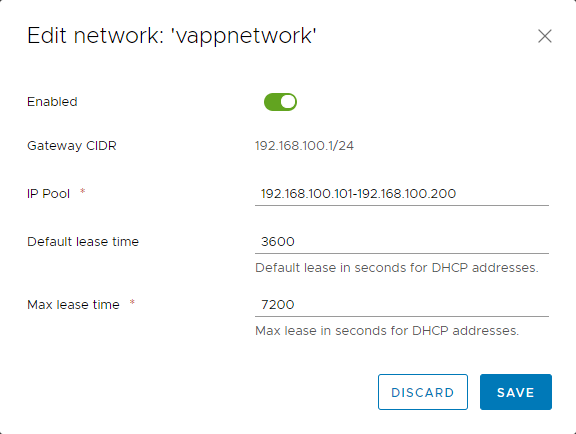
For more information about DHCP, see How to create a DHCP pool.
Creating firewall rules¤
There will be a rule in place to allow any traffic to traverse the firewall. You can amend or delete this rule or create new rules.
To create a firewall rule:
-
In the left navigation panel, select vApps.
-
In the card for the vApp, select Details.
-
Select the Networks tab.
-
Click your vApp network to view its network settings.
-
Select the Services tab.
-
Click Edit.
-
On the Firewall tab, click Add, specify the details for the firewall rule then click Save.
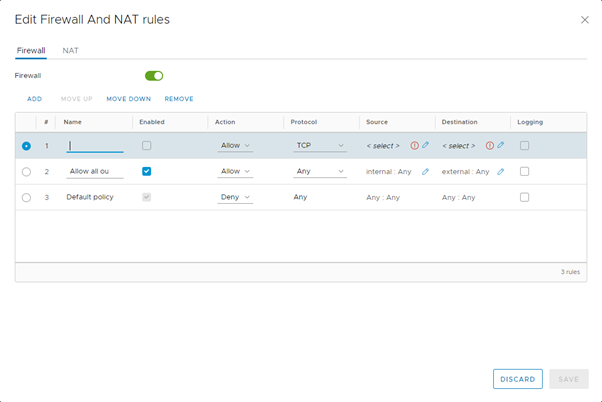
For more about firewall rules, see How to create firewall rules.
Creating NAT rules¤
NAT rules, enabled by default, enable mapping between internal VM interfaces and external IP addresses.
To edit the mapping rules for a VM:
-
In the left navigation panel, select vApps.
-
In the card for the vApp, select Details.
-
Select the Networks tab.
-
Click your vApp network to view its network settings.
-
Select the Services tab.
-
Click Edit.
-
On the NAT tab, click Add.
-
In the VM Interface field, click the edit (pencil) icon, then select the VM interface for which you want to add the NAT rule.
-
From the Mapping Mode list, select the mapping mode.
The default mapping is Automatic. You can change this to Manual, in which case, enter an External IP address to which the VM can map.
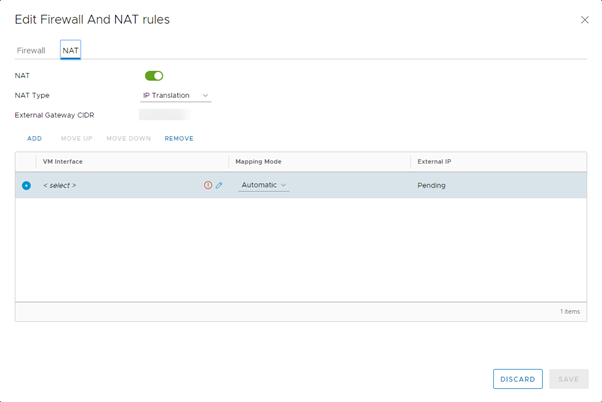
-
When you're done, click Save.
The external IP address will be on the same subnet as the VDC network that connects to the vApp edge.
For more information about NAT rules, see How to create NAT rules.
Creating static routes¤
Static routing at the vApp network level allows traffic to route between different vApp networks, across the VDC networks.
The prerequisites for static routing are as follows:
- Static routing must be enabled for the VDC network you're connecting to (see How to create a static route).
- The two vApp networks must be routed to the same VDC network.
- The vApp networks must be in vApps that have been started at least once.
To add a static route:
-
In the left navigation panel, select vApps.
-
In the card for the vApp, select Details.
-
Select the Networks tab.
-
Click the first vApp network to view its network settings.
-
Select the Routing tab.
-
Click Add.
-
In the Add Static Route dialog box, enter a Name for the static route.
-
Enter the following details:
- Network CIDR: The address of the first vApp network to which you're adding a static route
- Next Hop IP: The external IP address of that vApp network's router
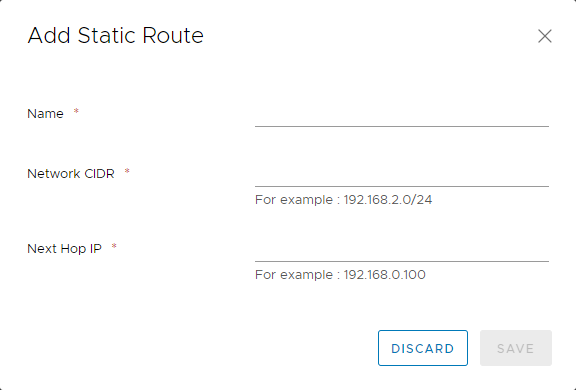
-
When you're done, click Save.
-
Repeat for the second vApp network.
The tables below provides examples of the settings needed to create a static route between two vApps.
Network Information
Network name Network specification Router external IP address vApp network 1 192.168.1.0/24192.168.0.100vApp network 2 192.168.1.0/24192.168.0.101VDC network shared 192.168.1.0/24N/A Static routing settings
Static route to network Route name Network Next hop IP address vApp network 1 To-vapp1 192.168.1.0/24192.168.0.100vApp network 2 To-vapp2 192.168.1.0/24192.168.0.101
vApp fencing¤
Fencing a vApp allows identical VMs within different vApps to be powered on without conflict, by isolating the MAC and IP addresses of the VMs. This feature is particularly useful if you are copying vApps or creating catalog images of vApps where these details can't be altered.
vApp fencing can be done during or after vApp creation. It is done when the VMs within the vApp sit on the VDC network, rather than on their own vApp network.
To apply vApp fencing during vApp creation:
-
In the left navigation panel, select vApps.
-
In the card for the vApp, select Details.
-
Select the Networks tab.
-
In the vApp Fencing section, click Edit.
-
Select the Fence vApp option then click OK.